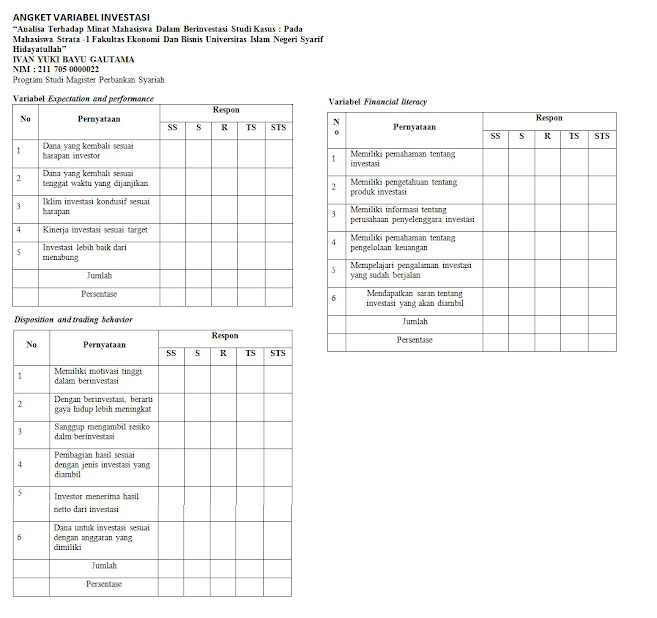
ANGKET VARIABEL INVESTASI
Sabtu, 27 Agustus 2022
Sabtu, 18 Juni 2022
Senin, 11 Mei 2020
PROPILEN GLIKOL
Etilen Glikol/propilen glikol
Meskipun digunakan dalam
kosmetik, sintesis kimia, dan aplikasi lain, kebanyakan etilena glikol digunakan
sebagai bahan utama formulasi antibeku dan antibodi untuk radiator mobil.
Etilen glikol (titik leleh, -13°C;
titik didih, 198°C) disintesis oleh oksidasi etilena menjadi etilen oksida,
diikuti oleh hidrolisis senyawa yang terakhir:
Paparan toksik terhadap etilen
glikol jarang terjadi karena tekanan uapnya yang rendah, tetapi terhirup tetesannya
bisa sangat berbahaya. Sejumlah besar kematian manusia yang disebabkan oleh keracunan
etilena glikol telah didokumentasikan. Dari terbatasnya informasi yang
tersedia, LD50 Untuk manusia diperkirakan sekitar 110 g. Etilen glikol yang
dicerna awalnya merangsang pusat sistem saraf, dan kemudian menekannya. Korban
dapat menderita asidemia dari kehadiran perantara asam glikolat metabolit.
Kerusakan ginjal terjadi kemudian, dan bisa berakibat fatal. Ginjal rusak karena
pengendapan kalsium oksalat padat, yang dihasilkan dari keseluruhan proses
berikut:
Perantara penting dalam proses ini adalah glikolaldehida,
glikolat, dan glioksilat:
Gagal ginjal dari pembentukan
metabolisme kalsium oksalat telah umum terjadi pada kucing spesies, yang
memiliki selera rakus untuk etilen glikol dalam antibeku. Deposit kalsium padat
oksalat juga telah diamati di hati dan jaringan otak korban keracunan etilen
glikol.
Manahan, Stanley E., Toxicological
chemistry and biochemistry, 2002:309
Gliserol MUNGKIN AMAN bila
diminum dalam waktu singkat. Gliserol dapat menyebabkan efek samping termasuk
sakit kepala, pusing, kembung, mual, muntah, haus, dan diare.
Minggu, 10 Mei 2020
Thermodynamic quantities of cell reactions
Thermodynamic
quantities of cell reactions
The
Gibbs free energy change at a given temperature for the overall cell reaction
for an electrochemical cell can be obtained from the reversible e.m.f. (E) of
the cell determined by Poggendorf’s compensation method.
ΔG=
–nF E
where
n is the number of faradays of electricity delivered by the cell. E is positive
by convention and being an intensive quantity, does not depend on how the
stoichiometric equation for the spontaneous overall cell reaction is written.
But ΔG being an extensive quantity does depend on how the overall cell reaction
is written. The same is true about the corresponding enthalpy and the entropy
changes (ΔH and ΔS). These thermodynamic quantities are usually expressed in kJ
mol–1 (ΔS in J K–1 mol–1) when these become intensive quantities.
From
thermo dynamics we have,
Δ
= – [ ∂ΔG/∂T]p
or
ΔS = nF[∂E/∂T]p
since
–ΔG = nF E
The
temperature coefficient of the cell e.m.f., (∂E/∂T)p can be obtained by
determining the e.m.f at various temperatures.
Again
from thermodynamics we have,
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Or
–n F E = ΔH – TΔS
or
ΔH = – n F E + TΔS
or ΔH =
– nF E + TnF [ ∂E/∂T]p
Thus
the enthalpy change associated with the overall cell reaction for a reversible cell
can be determined from the reversible e.m.f. (E) and the temperature
coefficient of the reversible e.m.f. of the cell, .The equilibrium constant is
related to standard Gibbs free energy, ΔGO
(or
– n F EO ). Hence we obtain
Since
ΔGO = – RT ln K
Or
– n F EO = – RT ln K
ln K = —[ nF EO/RT]
The
above equation enables one to calculate the equilibrium constant of an overall cell
reaction at a given temperature from the experimentally determined value of the
standard e.m.f. of the cell at the same temperature.
We
have seen earlier that the Weston Cadmium Cell has an e.m.f. (E) of 1.01463 V at
298 K and a temperature coefficient of -5.00 × 10–5 V K–1.
These two data help us to calculate the thermodynamic quantities of the overall
cell reaction.
ΔG
= – n F E
= – 2 × 96500 C mol–1 ×
1.01463 V
= –195824 Jmol-1
ΔS
= nF[ ∂ E/∂T]p
= 2 (96500 C mol–1) × (– 5.00 ×
10–5) V K–1
= – 9.65 Jmol-1
K–1
ΔH
= ΔG + T ΔS
= – 195824 Jmol-1
+
298 K (– 9.65 Jmol-1 K–1)
= -198700 Jmol-1
Electrochemistry II: Voltaic or Galvanic
cells
Suhaschandra Ghosh and Animesh Kumar
Rakshit, 2010, 16
FOOD PRESERVATIVE TEST
FOOD PRESERVATIVE TEST
Food additives (food additives)
are used so that food looks more attractive and durable; these ingredients can
be preservatives, colorings, flavorings and aromas, anti-oxidants, and others.
So the ingredient is not nutritionally valuable, but is added to food in the
manufacture or transportation to influence or maintain the special
characteristics of the food.
Some food additives have a bad
influence on human health; therefore the Ministry of Health has regulated /
stipulated the types of food additives that may and may not be used in food
processing. Additional ingredients that are prohibited from being used in food
are formalin (formaldehyde) and boric acid (the salt is sodium tetraborate /
borax).
BORAX
Borax is a sodium salt Na2B4O7.10H2O
which is widely used in various non-food industries, especially paper, glass,
solder, cleaning materials, wood preservatives, antiseptics, cockroach controls
and ceramics. The famous pyrex glass is made with a mixture of borax.
Borax is used as a solder,
cleaning agent, wood preservative, antiseptic and cockroach control. Borax is a
poisonous and dangerous material for humans, because it can cause toxic
effects, but the mechanism of toxicity is different from formaldehyde.
What is dangerous, borax can be
absorbed by the body and stored cumulatively in the liver, brain, intestines or
testicles so that the dose in the body becomes high. If consumed yearly can
cause cancer. Borax is also often misused in food. Usually added to crackers,
meatballs, rice cake and others. Laymen know borax by the name of Bleng
(Indonesian) or Cetitet.
Symptoms can include nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea, decreased body temperature, weakness, headaches,
erythermatous rash, and can even cause shock. Death in adults can occur in
doses of 15-25 grams, whereas in children in 5-6 grams doses. The danger of
Borax on health is absorbed through the intestines, damaged skin and mucous
membranes.
Following are some of the characteristics of foods
containing borax. Although it is not too typical but can help distinguish it
from food without borax.
a. Wet
noodles containing borax: The texture is very chewy, usually more shiny, not
sticky and does not break quickly.
b. Meatballs
contain borax: The texture is very chewy, the color is not brown like the use
of meat but is more likely to whitish
c. The
characteristics of crackers contain borax: The texture is very crispy, can give
a bitter taste
WHAT IS FORMALDEHYDE
Another name for formalin is
Formaldehyde or Metanal with the general formula HCHO. Formalin is a colorless
and pungent solution, at room temperature in the form of a gas that can
dissolve in alcohol, acetone or water.
In the chemical industry, it is
very important as a disinfectant, fungicide, bactericide, basic material for
making resins, preservatives of human beings / animals. Formaldehyde is a toxic
in humans that can cause: Abdominal pain, skin irritation, Lack of protein
(proteinuria), Excess acid (acidosis), Headaches to death, and Carcinogens /
causes of cancer.
BORAX TEST
Tests on borax containing samples
were carried out by adding 10 drops of conc. H2SO4 and 2
ml of methanol. Let stand for a while and then burned. This test produces the
same yellowish green color as the flame test of pure borax compounds. This
proves that the sample does indeed contain borax.
For test samples that do not
contain borask the procedure is carried out the same as in test samples
containing borax. But the results obtained do not cause a yellowish green
flame.
The other ways to test for the
presence of preservatives, especially borax, are:
To 0.5 ml the sample solution is
added:
a. Silver
nitrate, white sediment will occur from metaborac silver. In heating, black
Ag2O deposits will occur
b. Saturated
barium chloride, white barium metaborate will occur
FORMALIN TEST
A. Fehling Test
Take 10 grams of sample (tofu /
wet noodles / meatballs) then puree using a mortar. Add 10 ml of water, stir
until smooth. Then strain. Take ± 2ml of the filtered result, put it into a
test tube. Add 3 ml of Fehling's solution. Heat 5-10 minutes. Observe and
record the changes that occur. Solution contains formaldehyde if the initially
blue solution turns green and yellow or red precipitate is formed.
B. Potassium permanganate test
Test
tube containing 10 ml of milk spiked with 1 drop of 1N KMnO4
solution. The white milk solution will turn pink. The length of time the pink
color is lost from a drop of a potassium permanganate solution into a test tube
containing a sample of fresh milk is an indicator of possible formalin content
in the milk.
If
1 hour there is no change in color (stable pink) it means that the milk does
not contain formaldehyde (or rather say it does not use formaldehyde as a
preservative), and is followed by another series of tests before being declared
acceptable as raw material. If the pink color of the potassium permanganate
solution immediately fades / disappears to become colorless, it means there is
a possibility in milk samples containing formalin which is reacting to
eliminate the color (reducing) potassium permanganate.
False
positive (false results) can occur if the food contains other reducing agents
that react with potassium permanganate such as oxalic acid, etc. But most of
the preserved foods are plant / animal foods (wet fish, meatballs, tofu) that
have high protein content are very unlikely to contain oxalic acid naturally.
Assessment Of Learning
Assessment Of Learning
1.
Definition of Learning Assessment
From the point of view of
language, judgment is defined as the process of determining the value of an
object. To be able to determine a value or price of an object requires the size
or criteria. For example, to be able to say good, moderate, less, there needs
to be a clear measure of how good, medium, and less. The measure is called the
criterion. From this understanding, it can be said that the characteristics of
assessment are the existence of the object or program being assessed and the
existence of criteria as a basis for comparing what is achieved with the
criteria that must be achieved. Comparison can be absolute, it can also be relative.
Comparison is absolute meaning
that the results of the comparison describe the position of the object being
evaluated in terms of applicable criteria. While the relative comparison means
the result of the comparison is more describing the position of an object that
is valued against other objects based on the same criteria. Thus, the core
assessment is the process of determining the value of a particular object based
on certain criteria. The process of giving value takes place in the form of
interpretation which ends with judgment. Interpretation and judgement is a
theme of assessment that implies a comparison between criteria and reality in
the context of a particular situation. On that basis, in the assessment
activities there are always objects / programs that are assessed, there are
criteria, and there are interpretations / judgments.
Assessment of learning outcomes is
the process of assigning grades to learning outcomes achieved by students with
certain criteria. This implies that the object judged is the result of student
learning. Student learning outcomes are essentially change in behavior.
Behavior as a result of learning in a broad sense covers the fields of
cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Therefore, in the assessment of learning
outcomes the formulation of abilities and behaviors desired by students
(competence) becomes an important element as a basis and reference for
assessment. Assessment of the learning process is an effort to give value to
teaching and learning activities carried out by students and teachers in
achieving teaching objectives.
2.
Learning Assessment Function
The purpose of learning is
essentially a change in behavior in students. Therefore, the assessment should
be examined to what extent changes in student behavior have occurred through
the learning process. For example by making changes in teaching strategies,
providing guidance and learning assistance to students. In other words, the
results of the assessment are not only useful for knowing whether changes in
student behavior have been achieved, but also as feedback for efforts to
improve the learning process.
In this assessment seen the
extent to which the effectiveness of the learning process in seeking changes in
student behavior. Therefore, the assessment of learning outcomes and processes
are interrelated with each other because the learning outcomes achieved by
students are a result of the learning process that they go through (their
learning experiences). In line with the above understanding, the evaluation
functions as follows:
a. Tool
to find out whether learning objectives are achieved. With this function then
the assessment must refer to the formulations of learning objectives as a
translation of the subject competencies.
b. Feedback
for improving the teaching and learning process. Improvements might be made in
terms of learning objectives, student learning activities or experiences,
learning strategies used by the teacher, learning media, etc.
c. The
basis for compiling reports on student learning progress to his parents. In the
report, students' ability and study skills were expressed in various fields of
study or subjects in the form of achievement values.
3.
Purpose of Learning Assessment
In line with the assessment
function above, the purpose of the assessment of learning outcomes is to:
a.
Describe students' learning skills so that their
strengths and weaknesses can be identified in various fields of study or
subjects they take. By describing the skills, it can also be seen the position
of the ability of students compared to other students
b.
Knowing the success of the education and
learning process in school, in aspects of intellectual, social, emotional,
moral, and skills, namely how far the effectiveness in changing the behavior of
students towards the expected educational goals. The success of education and
learning is important, considering its role as an effort to humanize or
civilize humans, in this case students to become qualified human beings
c.
Determine the follow-up of the results of the
assessment, namely to make improvements and improvements in terms of education
and learning programs and their implementation strategies. Failure of students
in learning outcomes they achieve should not be seen as lacking solely in
students themselves, but can also be caused by learning programs that are given
to them or by strategic mistakes in executing these programs. For example,
inaccuracies in choosing and use teaching methods and learning aids
d.
Provide accountability (accountability) from the
school to the parties concerned. The parties in question include the
government, the community, and parents of students. In accounting for the
results it has achieved, the school reports various strengths and weaknesses in
the implementation of the education system and the obstacles it faces. Reports
are submitted to interested parties, for example the local education office
through officers who handle it. While accountability to the community and
parents is conveyed through student learning progress reports (report cards) at
the end of each program/semester
4.
Principles of Learning Assessment
In addition to the purpose and
function of assessment, teachers must also understand the principles of
assessment. The principles of assessment referred to include the following:
a. Assessment
of learning outcomes should be an integral part of the learning process. This
means that every teacher carrying out the learning process he must carry out
assessment activities. The intended evaluation is formative assessment. There
is no learning process without assessment. Thus the progress of student
learning can be known and the teacher can always improve the quality of the
learning process carried out.
b. Assessment
of learning outcomes should be clearly designed what abilities should be
assessed, the material or content of the teaching material being tested, the
assessment tools to be used, and the interpretation of the results of the
assessment. As a benchmark or signs in designing assessment of learning
outcomes is a curriculum that applies primarily the objectives and competencies
of subjects, the scope of the content or teaching material and guidelines for
its implementation.
c. The
assessment must be carried out comprehensively, meaning that the abilities
measured include cognitive, affective and psychomotor aspects. In cognitive
aspects include: knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis,
and evaluation proportionally.
d. Assessment
tools must be valid and reliable. Valid means measuring what should be measured
(accuracy). Reliability means that the results obtained from the assessment are
consistent or consistent.
e. Assessment
of learning outcomes should be followed by no further. Assessment data is very
useful for teachers as material to perfect learning programs, improve learning
weaknesses, and tutoring activities for students who need them.
f. Assessment
of learning outcomes must be objective and fair so that they can describe the
actual abilities of students.
Indonesian Education Ministry, 2008
Sabtu, 03 Maret 2018
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)